1. Stack과 Queue
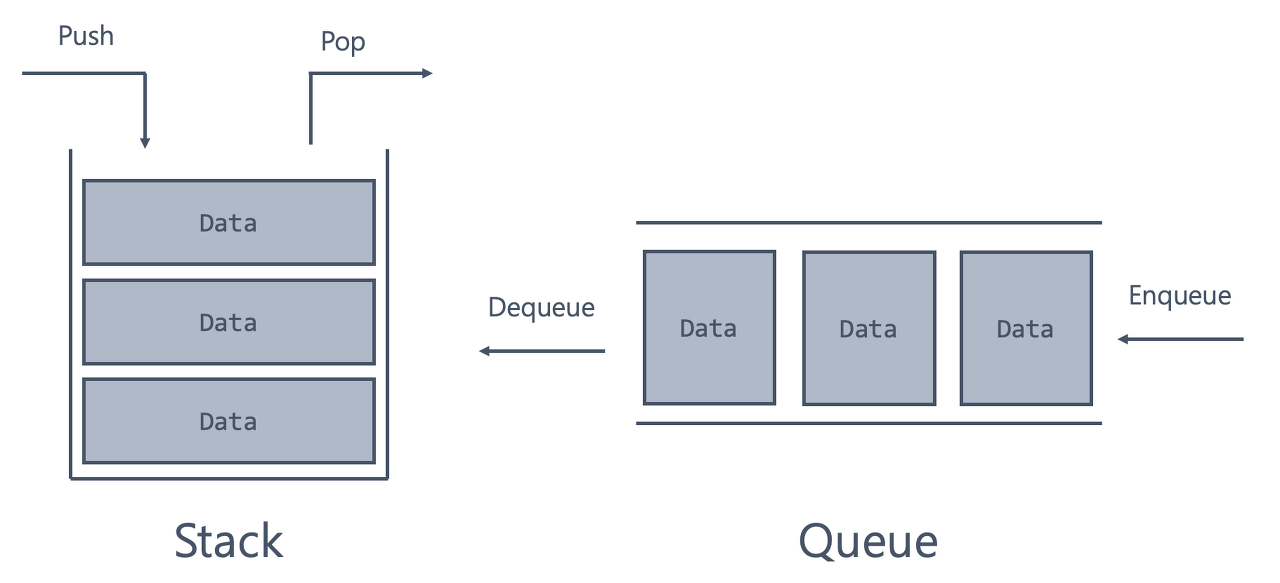
스택은 마지막에 저장한 데이터를 가장 먼저 꺼내는 LIFO(Last In First Out)의 구조리며, 큐는 처음에 저장한 데이터를 가장 먼저 꺼내게 되는 FIFO(FIrst In FIrst Out)의 구조이다.
예를 들면 스택은 웹 브라우저의 방문기록 (뒤로가기), 나중에 실행된 것부터 나중에 취소하는 실행 취소와 같은 곳에 활용할 수 있다. 큐는 프린터의 인쇄 대기열같은 우선순위가 같은 작업 예약, 프로세스 관리와 같은 입력 순서대로 처리해야할 필요가 있는 상황에 이용한다.
- Stack 메서드
| 메서드 | 설명 |
| boolean empty() | Stack이 비어있는지 알려준다 . |
| Object peek() | Stack의 맨 위에 저장된 객체를 반환. pop과 달리 Stack에 객체를 꺼내지는 않는다. |
| Object pop() | Stack의 맨 위에 저장된 객체를 꺼낸다. (비었을때는 EmptyStackException이 발생) |
| Object push(Object item) | Stack에 객체를 저장한다. |
| int search(Object o) | Stack에서 주어진 객체를 찾아서 그위치를 반환, 못찾으면 -1을 반환한다. 배열과 달리 위치는 0이 아닌 1부터 시작 |
- Queue 메서드
| 메서드 | 설명 |
| boolean add() | 지정된 객체를 Queue에 추가한다. |
| Object remove() | Queue에 객체를 꺼내 반환. (비어있으면 NoSuchElementException이 발생) |
| Object element() | 삭제없이 요소를 읽어온다. peek()와 달리 Queue가 비었을 때 NoSuchElementException 발생 |
| boolean offer(Object o) | Queue에 객체를 저장. 성공하면 true, 실패하면 false |
| Object poll() | Queue에서 객체를 꺼내서 반환. 비어있으면 null 반환 |
| Object peek() | 삭제없이 요소를 읽어온다. Queue가 비어있으면 null 반환 |
public static void main(String[] args) {
//stack과 Queue 선언
Stack<Object> st = new Stack<>();
Queue<Object> q = new LinkedList<>(); //Queue 인터페이스의 구현체인 LinkedList를 사용
st.push("A");
st.push("B");
st.push("C");
q.add("A");
q.add("B");
q.add("C");
while (!st.empty()){
System.out.println(st.pop()); //C, B, A
}
while (!q.isEmpty()){
System.out.println(q.poll()); //A, B, C
}
}자바에서는 스택을 Stack클래스로 구현하려 제공하고 있지만 큐는 Queue 인터페이스로만 정의해 놓았을 뿐 별도의 클래스를 제공하고 있지 않다. 대신 Queue 인터페이스를 구현한 클래스들이 있어 이 들 중의 하나를 선택해서 사용하면 된다. Queue 의 경우 엄밀히 말하면 List 인터페이스에 포함되어 있지 않다 .
자바에서 LinkedList는 Linst를 구현하기도 하지만 Queue의 Deque 클래스를 구현하기도 한다.
public class LinkedList<E>
extends AbstractSequentialList<E>
implements List<E>, Deque<E>, Cloneable, java.io.Serializable { } //이 부분
참고로 인터페이스는 설계도, 구현체는 인터페이스를 구현한 클래스라는 뜻이다. (= 구현 클래스 or 실체클래스)
1.2 스택과 큐의 활용
스택 : 웹브라우저의 뒤로/ 앞으로 , 수식계산 및 수식괄호검사
큐: 최근사용문서 , 인쇄작업 대기목록
- 웹 브라우저 뒤로/앞으로 예제
public class StackEx1 {
//두 개의 스택 선언
public static Stack<String> back = new Stack<>();
public static Stack<String> forward = new Stack<>();
public static void main(String[] args) {
goURL("1.네이트");
goURL("2.야후");
goURL("3.네이버");
goURL("4.다음");
printStatus();
goBack();
System.out.println(" = 뒤로 버튼을 누른 후= ");
printStatus();
goBack();
System.out.println(" = 뒤로 버튼을 누른 후= ");
printStatus();
goForward();
System.out.println(" = 앞으로 버튼을 누른 후= ");
printStatus();
goURL("www.hi.com");
System.out.println(" = 새로운 주소로 이동 후= ");
printStatus();
}
public static void printStatus() {
System.out.println("back:" + back);
System.out.println("forward:" + forward);
System.out.println("현재 화면은 '" + back.peek() + "' 입니다.");
System.out.println();
}
public static void goURL(String url) {
back.push(url);
if (!back.isEmpty()) {
forward.clear();
}
}
public static void goForward() {
if (!forward.empty()) {
back.push(forward.pop());
}
}
public static void goBack() {
if (!back.isEmpty()) {
forward.push(back.pop());
}
}
}
- 수식 괄호 체크
public class ExpValidStack {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//수식의 괄호의 쌍이 맞는지
Stack<String> st = new Stack<>();
String expression = "((2+3) *1) + 3";
try {
for (int i = 0; i < expression.length(); i++) {
char ch = expression.charAt(i);
if (ch == '(') {
st.push(ch + ""); //넣고
} else if (ch == ')') {
st.pop();// 꺼내고
}
}
if (st.isEmpty()) { //비어있으면 괄호가 맞다는 의미니까
System.out.println("괄호가 일치합니다.");
} else {
System.out.println("괄호가 일치하지 않습니다.");
}
} catch (EmptyStackException e) { //비어있는데 pop하면 발생하는 에러
System.out.println("괄호가 일치하지 않습니다.");
}
}
}
- 유닉스의 history 명령어를 queue를 이용해서 구현
public class QueueEx1 {
static Queue<String> q = new LinkedList<>();
static final int MAX_SIZE = 5;
public static void save(String input) {
//queue에 저장
if (!"".equals(input)) {
q.offer(input);
}
//queue의 최대 크기를 넘으면 제일 처음 입력된 것을 삭제 - 무조건 5개만 저장가능
if (q.size() > MAX_SIZE) {
q.remove();
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
System.out.println("help를 입력하면 도움말을 볼 수 있습니다.");
while (true) {
System.out.print(">>");
try {
Scanner s = new Scanner(System.in);
String input = s.nextLine().trim();
if ("".equals(input)) {
continue;
}
if (input.equalsIgnoreCase("q")) {
System.exit(0); //프로세스 강제 정상종료
} else if (input.equalsIgnoreCase("help")) {
System.out.println("help - 도움말을 보여줍니다.");
System.out.println("q 또는 Q - 프로그램을 종료합니다.");
System.out.println("history - 최근에 입력한 명령어를 " + MAX_SIZE + "개 보여줍니다.");
} else if (input.equalsIgnoreCase("history")) {
int i = 0;
//입력어 저장
save(input);
//LinkedList의 내용을 보여준다.
LinkedList tmp = (LinkedList) q;
ListIterator it = tmp.listIterator();
while (it.hasNext()) {
System.out.println(++i + "." + it.next());
}
} else {
save(input);
System.out.println(input);
}
} catch (Exception e) {
System.out.println("입력 오류입니다.");
}
}
}
}
PriorityQueue
Queue 인터페이스의 구현체(인터페이스를 구현한 클래스)중 하나로 저장한 순서에 관계없이 우선순위가 높은 것부터 꺼내게 된다. 우선순위 queue는 값을 비교해야하므로 null은 저장할 수 없다. null을 저장하면 NullPointException이 발생한다.ㅣ
저장공간으로 배열을 사용하며 각 요소를 힙(heap) 이라는 자료구조의 형태로 저장한다. 힙은 이진트리의 한 종류로가장 큰 값이나 가장 작은 값을 빠르게찾을 수 있다는 특징이 있다.
public class PriorityQueueEx {
public static void main(String[] args) {
PriorityQueue<Integer> pq = new PriorityQueue<>();
pq.offer(1);
pq.offer(3);
pq.offer(2);
pq.offer(5);
pq.offer(4);
System.out.println(pq); //저장순서 출력 1,3,2,5,4,
//내부적으로 힙 자료구조로 저장
while (!pq.isEmpty()){
System.out.println(pq.poll())//출력 1,2,3,4,5
}
}
}
Deque (Double- Ended Queue)
Queue의 변형으로, 한쪽 끝으로만 추가/삭제할 수 있는 Queue와 달리 Dequeue(덱 또는 디큐)는 양쪽 끝에 추가/삭제가 가능하다. 구현체로는 ArrayDeqe와 LinkedList가 있다.

덱은 스택과 큐를 하나로 합쳐놓은 것과 같으며 스택으로도 , 큐로도 사용할 수 있다.
출처 : 자바의 정석
'Java' 카테고리의 다른 글
| [JAVA] TreeSet (0) | 2023.12.07 |
|---|---|
| [Java] HashSet (0) | 2023.12.06 |
| [Java] LinkedList (1) | 2023.12.06 |
| [Java] ArrayList (1) | 2023.12.06 |
| [Java] 컬렉션 프레임워크 (Collection Framework) (1) | 2023.12.06 |